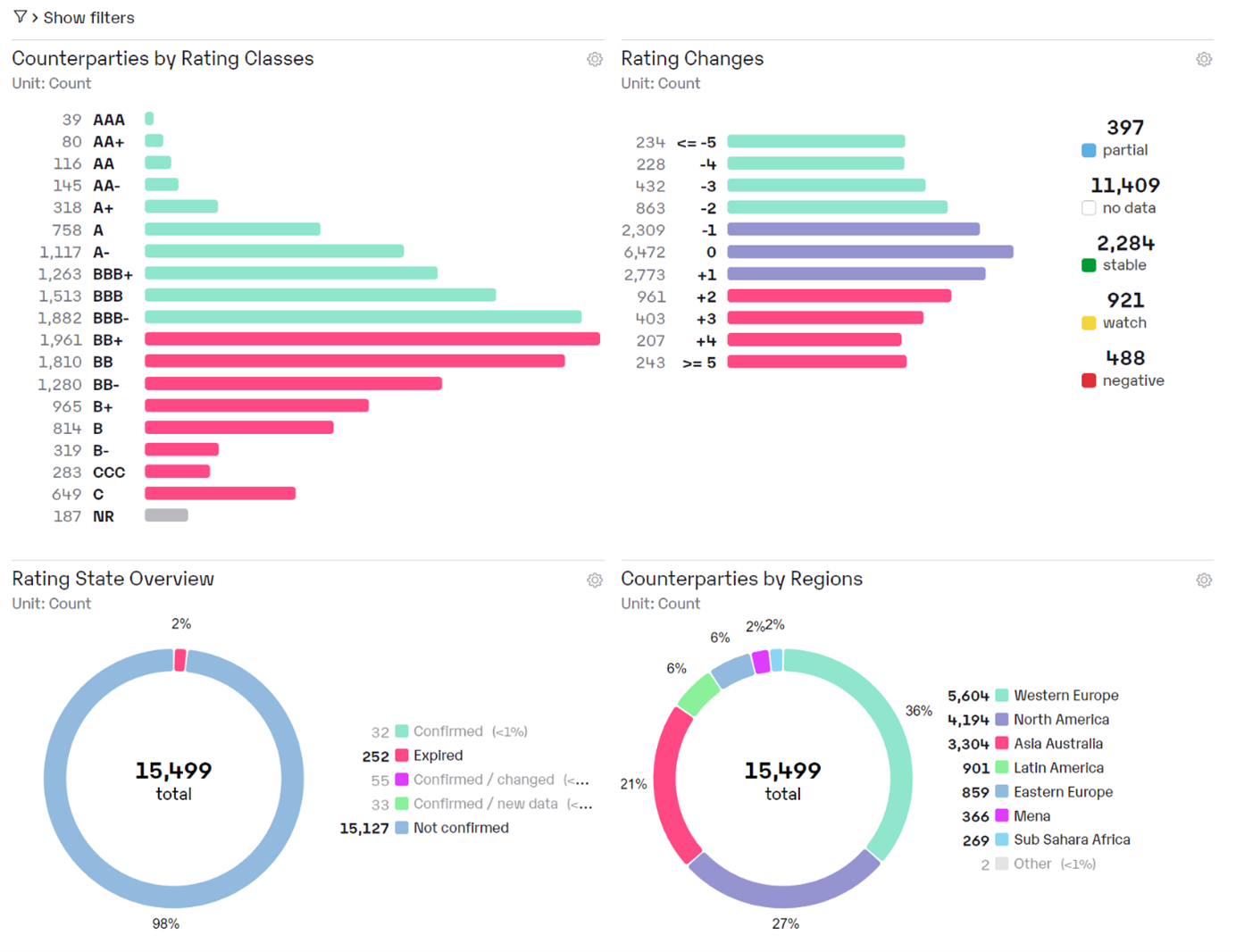
Risk management comprises all measures taken by a company or organization to identify, measure, monitor and control risks.
The aim is to minimize potential losses and ensure stable and sustainable business development. Risk management is thus a central task. An important component of risk management is risk analysis, in which the various risks are identified and assessed. Based on this, strategies are developed to minimize and manage risks. These include, for example, setting risk limits, diversifying risks and using derivatives to hedge risks.
Another task of risk management is to monitor compliance with regulatory requirements and internal guidelines. These include, for example, compliance with minimum capital requirements or the limitation of risk positions.
Effective risk management requires a high level of employee qualification and expertise as well as close cooperation between the bank's various departments. These include, in particular, risk management, controlling, the business areas, and treasury.
The importance of risk management has increased sharply, particularly since the financial crisis of 2008. Regulators around the world have since tightened the requirements for risk management at banks and issued a large number of regulations to make the financial system more stable and prevent future crises.