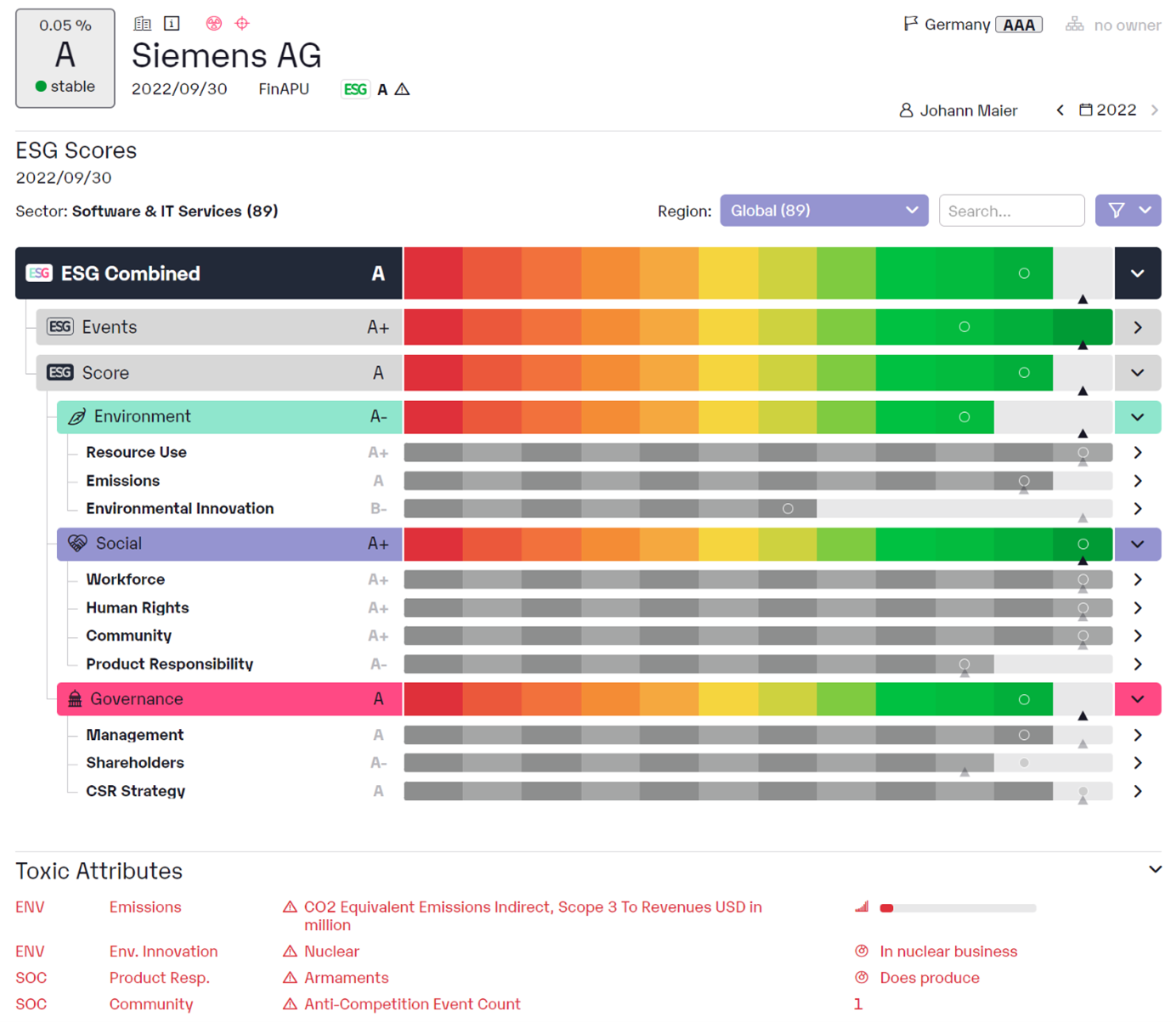
ESG is a concept of sustainability that refers to environmental, social and governance factors.
It is increasingly used by companies and investors as an important assessment criterion to evaluate the risk and return of investments. Only an integrated approach across ESG performance, cash flow assessment and accurate return projections allows for a deep understanding of sustainability performance that a company delivers.
The environmental component of ESG refers to a company's impact on the environment. This includes issues such as energy efficiency, CO2 emissions, water and waste management, and the use of renewable resources. The social component of ESG refers to a company's impact on its employees, customers and communities. This includes issues such as human rights, working conditions, diversity and inclusion, and social engagement. The governance component of ESG refers to the leadership and management of a company. This includes issues such as corporate governance, ethics, transparency and disclosure.
ESG criteria can be taken into account by investors when selecting investments to ensure that they are investing in companies that are sustainable and have a long-term focus. Companies that integrate ESG factors into their business practices can create long-term value by gaining the trust and loyalty of customers and investors and avoiding potential reputational risks.
Governments and regulators have also begun to integrate ESG criteria into their decision-making processes. This can help encourage companies and investors to promote sustainability and have a positive impact on the environment and society as a whole.
ESG has gained importance in recent years and is expected to become even more prominent in the focus of companies and investors in the future. The measurement and reporting of ESG criteria will continue to evolve, and companies that apply sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive advantage.